Dynamic Disk and Basic Disk
Dynamic disk and basic disk are two storage types of hard disk configurations. Today let’s look together what is dynamic disk and what is basic disk. In addition, what’s the difference between them?
Basic Disk
Basic disk uses partitions to manage data. Basic disk supports two partition styles-MBR and GPT.
Partition Styles
MBR Disk
On MBR disk, there are primary partition, extended partition and logical partition. MBR disk allows creating 4 primary partitions or 3 primary partitions and 1 extended partitions where 128 logical partitions can be created at most in Windows operating system.
You can extend primary partition by taking space from contiguous unallocated space which is next to it. Certainly, logical partition can also be extended with adjacent free space in the extended partition.
GPT Disk
While on GPT disk, there is no difference between partition names. They all called GPT partitions whose function is the same with primary partition. Moreover, GPT disk does not have a limitation on partition number.
Dynamic Disk
Dynamic disk was first introduced when Windows 2000 was released. Compared with basic disk, dynamic disk has many new features. You can create different types of volumes on dynamic disk.
Volume Types
1. Simple Volume: Simple volume is like primary partition on basic disk. And you can create lots of simple volumes on a dynamic disk. You can only create simple volume when you have one dynamic disk.
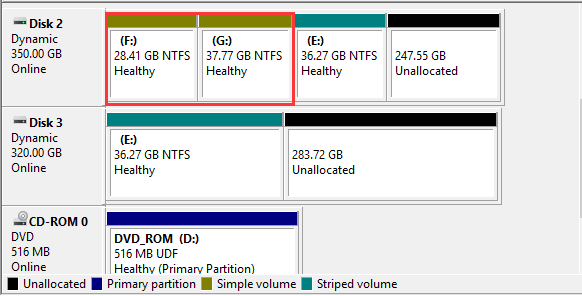
2. Striped Volume: To create striped volume, you need at least two disks and the unallocated space must be the same size. However, striped volume doesn’t provide fault tolerance.
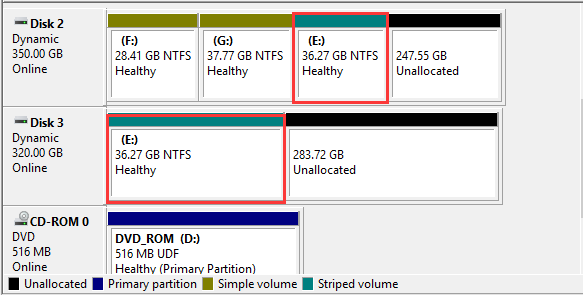
3. Spanned Volume: Spanned volume combines two or more disks’ unallocated space into one volume. The size of each unallocated space can be different. Hence, it can take full advantage of disk space. But it is a non-fault-tolerance disk.
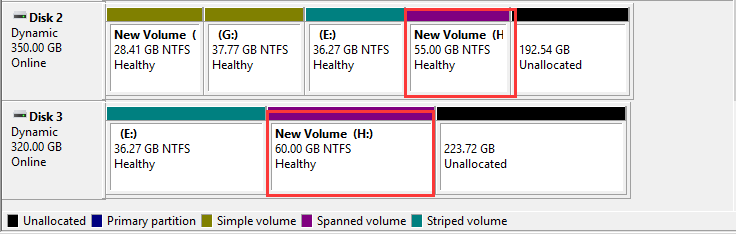
4. Mirrored Volume: Mirrored volume needs two disks with same size of unallocated space. It is a fault-tolerance disk. If one of the disks fails, the data on the failed disk will not be available, but the system can continue to run using the normal disk. Conversely, it is a disadvantage too. Mirrored volume waste disk size and its disk utilization rate is 50%.
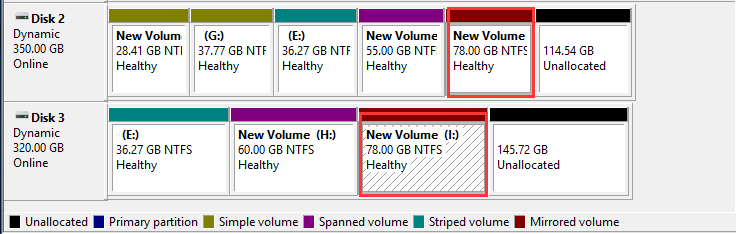
5. RAID-5 Volume: RAID-5 Volume can be created with 3 or more disks with the same size. It provides fault-tolerance. In addition, it’s read performance is improved compared with mirrored volume.
Difference Between Basic Disk and Dynamic Disk
Supported operating system: All Windows versions support basic disk. While dynamic disk is only supported by Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7/8, Windows 10 and Windows Server editions. But Windows XP does not support mirrored volume and RAID- 5 volume.
Extend Partition: Partition on basic disk can be extended under the circumstance that there is unallocated space right to the partition. Otherwise, you will find the extend volume greyed out. As to dynamic disk, volume can be extended even no unallocated space is adjacent to it.
Partition Location: Partition must be in the same disk on basic disk. On dynamic disk, a volume can be spanned in different disks.
Volume Type: Partitions on basic disk called primary partition, logical partition and extended partitions. But on dynamic disk, they are called volumes, simple volume, mirrored volume, spanned volume, etc.
Conversion: Basic disk can be converted to dynamic disk easily with Windows built-in Disk Management. There is no need to restart your computer. But once you convert a basic disk to dynamic, it’s not easy to convert it back. You need to delete all volumes on dynamic disk or turn to third party partition manager like MiniTool Partition Wizard without deleting volumes.
Top Recommendation
If you want to convert dynamic disk to basic, read A Powerful Dynamic Disk Partition Manager.
In this post, I tell you the difference between dynamic disk and basic disk and partition styles on basic disk and volume types on dynamic disk. Which type do you like to use?
Server Partition Manager Resources
Server Partition Manager - Paragon
- How to Make Automatic Backup
- Restore System to Dissimilar Hardware
- Migrate Windows 10 to SSD
- Merge Partitions Without Losing Data
- Recover Data from Hard Drive Won’t Boot
- External Hard Drive Not Accessible
- File System
- HDD VS SSD
- Dynamic Disk and Basic Disk
- Clone Hard Drive to SSD
- Paragon Partition Manager Personal
- Paragon Partition Manager Server
Server Partition Manager - Partition
- Partition Manager 8.5 Enterprise Server Edition
- Partition Manager Enterprise Server
- Partition Manager Enterprise Server Edition
- Partition Manager for Windows Server 2003
- Partition Manager Server
- Partition Manager Server 2003
- Partition Manager Server Edition
- Partition Manager Software
- Partition Manager Windows 2000
- Partition Manager Windows 2000 Server
- Partition Manager Windows 2003
- Partition Manager Windows 2003 Server
- Partition Manager Windows 2008
- Server Partition Manager